mathjax2mobi:将包含MathJax方程的HTML转换为电子书格式
Home
项目简介
先大致讲讲项目情况。

做完项目后,有点开心。写下了这样一段话。
写了一天代码,终于得到了漂亮的费曼物理讲义电子书!费曼物理讲义公开在网上,是用latex渲染的。人们常用latex来写论文,它对数学公式的渲染很棒。而公开在网上,用到了mathjax这个库。它把latex源码变成了html代码,生成了很多的div和span标签。电子书却不支持这种方式。这时,想法是抓取网页,逆向mathjax渲染,接着替换成svg图片。出现了挺多问题,一个是源码有很多的latex自定义宏,需要加上;第二个是内嵌很多svg会有问题。如果是单个svg倒没问题,很多的时候会出现问题。大概是浏览器和svg的诡异Bug。这时只要把svg保存为文件,用img标签引入进来即可。公式也分为两种,一种是文本中间的公式,一种是单行的公式。所以,最后就得到了漂亮的电子书!
查询的资料
这里记录了解决项目过程中访问的资料。因为这是一个教程,所以向学生展示一下大概做一个项目是怎么样的体验。
开始项目
费曼物理讲义已经在公开在网上可以阅读。我想在Kindle上看它。然而因为它有挺多的数学公式。它最初的稿子应该是用latex做的。它用mathjax这个库来把latex格式的内容显示在网页上。
举个例子。
<span class="MathJax_Preview" style="color: inherit; display: none;">
</span>
<div class="MathJax_Display">
<span class="MathJax MathJax_FullWidth" id="MathJax-Element-10-Frame" tabindex="0" style="">
<span class="mi" id="MathJax-Span-159" style="font-family: MathJax_Math-italic;">d<span style="display: inline-block; overflow: hidden; height: 1px; width: 0.003em;">
</span>
</span>
</div>
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-10">\begin{equation}
\label{Eq:I:13:3}
dT/dt = Fv.
\end{equation}
</script>
上面是截取的一段html代码。这一块html代码中。script标签下是latex的原样文本。mathjax把它变成很多的span。来显示它。
我们现在有个思路。就是把mathjax的显示方法改成svg图片。
从 GitHub 上找到一个项目tuxu/latex2svg。
from latex2svg import latex2svg
out = latex2svg(r'\( e^{i \pi} + 1 = 0 \)')
print(out['depth'])
print(out['svg'])
试着运行,但出错了。
raise RuntimeError('latex not found')
RuntimeError: latex not found
看看代码。
# Run LaTeX and create DVI file
try:
ret = subprocess.run(shlex.split(params['latex_cmd']+' code.tex'),
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
cwd=working_directory)
ret.check_returncode()
except FileNotFoundError:
raise RuntimeError('latex not found')
原来这也依赖于latex命令。
安装一下。
brew install --cask mactex
==> Caveats
You must restart your terminal window for the installation of MacTex CLI tools to take effect.
Alternatively, Bash and Zsh users can run the command:
eval "$(/usr/libexec/path_helper)"
==> Downloading http://mirror.ctan.org/systems/mac/mactex/mactex-20200407.pkg
==> Downloading from https://mirrors.aliyun.com/CTAN/systems/mac/mactex/mactex-20200407.pkg
######################################################################## 100.0%
All formula dependencies satisfied.
==> Installing Cask mactex
==> Running installer for mactex; your password may be necessary.
installer: Package name is MacTeX
installer: choices changes file '/private/tmp/choices20210315-4643-5884ro.xml' applied
installer: Installing at base path /
installer: The install was successful.
🍺 mactex was successfully installed!
安装成功。
% latex
This is pdfTeX, Version 3.14159265-2.6-1.40.21 (TeX Live 2020) (preloaded format=latex)
restricted \write18 enabled.
**
out = latex2svg(r'\( e^{i \pi} + 1 = 0 \)')
print(out['depth'])
print(out['svg'])
svg = open('1.svg', 'w')
svg.write(out['svg'])
svg.close()
可以生成svg了。
所以试试把mathjax中得到的latex文本都生成一下。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from latex2svg import latex2svg
file = open('The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 13_ Work and Potential Energy (A).html')
content = file.read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
mathjaxs = soup.findAll('script', {'type': 'math/tex'})
for mathjax in mathjaxs:
print(mathjax.string)
out = latex2svg(mathjax.string)
print(out['svg'])
可惜出错了。
raise CalledProcessError(self.returncode, self.args, self.stdout,
subprocess.CalledProcessError: Command '['latex', '-interaction', 'nonstopmode', '-halt-on-error', 'code.tex']' returned non-zero exit status 1.
具体哪个公式错了呢。
\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2
latex
来学习一下latex。
\documentclass[12pt]{article}
\usepackage{lingmacros}
\usepackage{tree-dvips}
\begin{document}
\section*{Notes for My Paper}
Don't forget to include examples of topicalization.
They look like this:
{\small
\enumsentence{Topicalization from sentential subject:\\
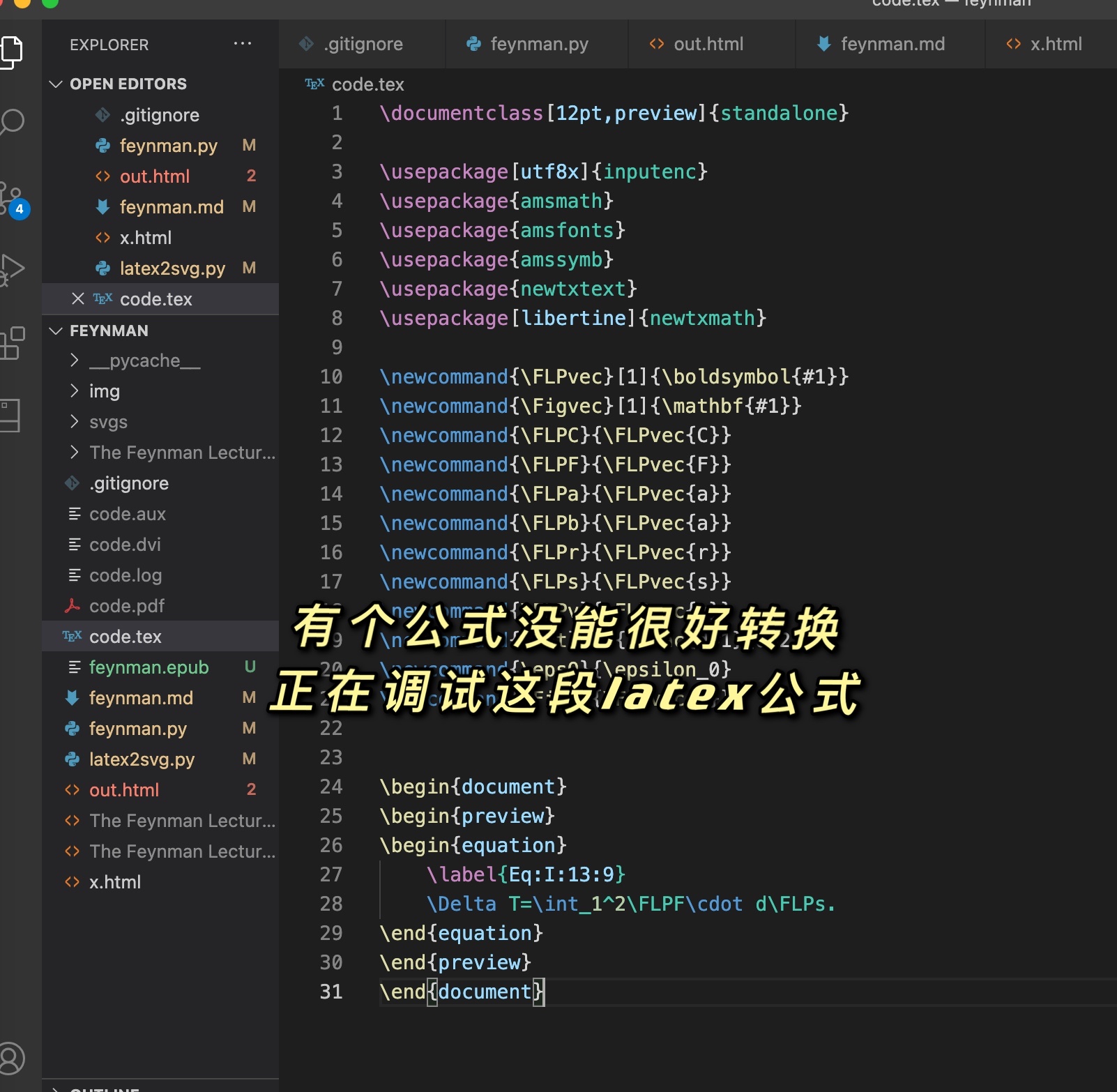
\shortex{7}{a John$_i$ [a & kltukl & [el &
{\bf l-}oltoir & er & ngii$_i$ & a Mary]]}
{ & {\bf R-}clear & {\sc comp} &
{\bf IR}.{\sc 3s}-love & P & him & }
{John, (it's) clear that Mary loves (him).}}
}
\subsection*{How to handle topicalization}
I'll just assume a tree structure like (\ex{1}).
{\small
\enumsentence{Structure of A$'$ Projections:\\ [2ex]
\begin{tabular}[t]{cccc}
& \node{i}{CP}\\ [2ex]
\node{ii}{Spec} & &\node{iii}{C$'$}\\ [2ex]
&\node{iv}{C} & & \node{v}{SAgrP}
\end{tabular}
\nodeconnect{i}{ii}
\nodeconnect{i}{iii}
\nodeconnect{iii}{iv}
\nodeconnect{iii}{v}
}
}
\subsection*{Mood}
Mood changes when there is a topic, as well as when
there is WH-movement. \emph{Irrealis} is the mood when
there is a non-subject topic or WH-phrase in Comp.
\emph{Realis} is the mood when there is a subject topic
or WH-phrase.
\end{document}
网上找到一段样例的latex源码。
% latex code.tex
This is pdfTeX, Version 3.14159265-2.6-1.40.21 (TeX Live 2020) (preloaded format=latex)
restricted \write18 enabled.
entering extended mode
(./code.tex
LaTeX2e <2020-02-02> patch level 5
L3 programming layer <2020-03-06>
(/usr/local/texlive/2020/texmf-dist/tex/latex/base/article.cls
Document Class: article 2019/12/20 v1.4l Standard LaTeX document class
(/usr/local/texlive/2020/texmf-dist/tex/latex/base/size12.clo))
(/usr/local/texlive/2020/texmf-dist/tex/latex/tree-dvips/lingmacros.sty)
(/usr/local/texlive/2020/texmf-dist/tex/latex/tree-dvips/tree-dvips.sty
tree-dvips version .91 of May 16, 1995
) (/usr/local/texlive/2020/texmf-dist/tex/latex/l3backend/l3backend-dvips.def)
(./code.aux) [1] (./code.aux) )
Output written on code.dvi (1 page, 3416 bytes).
Transcript written on code.log.

来对着源码和渲染后的效果,看看能学到什么。
\begin{document}
\end{document}
这样来把文档裹起来。
\section*{Notes for My Paper}
这表示section标题开头。
\subsection*{How to handle topicalization}
这表示子标题。
\shortex{7}{a John$_i$ [a & kltukl & [el &
{\bf l-}oltoir & er & ngii$_i$ & a Mary]]}
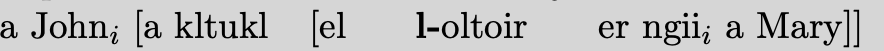
可见$_i$来表示下标。{\bf l-}来表示加粗。
\enumsentence{Structure of A$'$ Projections:\\ [2ex]
\begin{tabular}[t]{cccc}
& \node{i}{CP}\\ [2ex]
\node{ii}{Spec} & &\node{iii}{C$'$}\\ [2ex]
&\node{iv}{C} & & \node{v}{SAgrP}
\end{tabular}
\nodeconnect{i}{ii}
\nodeconnect{i}{iii}
\nodeconnect{iii}{iv}
\nodeconnect{iii}{v}
}
注意到nodeconnect来表示连线。
latex 转换成 svg
继续项目。
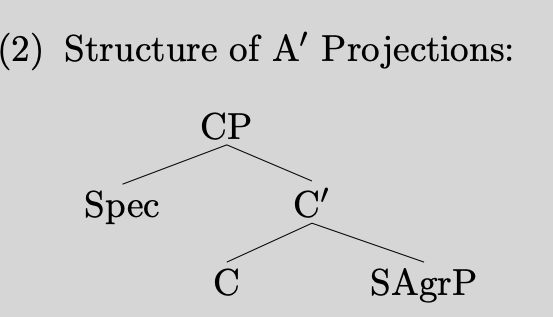
\documentclass[16pt]{article}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\begin{document}
\[\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2\]
\end{document}
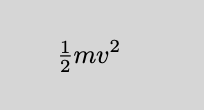
这样可以正确地被渲染。在代码里无法被渲染,可能是因为没有加上\usepackage{amsmath}。
\documentclass[12pt,preview]{standalone}
\usepackage[utf8x]{inputenc}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage{amsfonts}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\usepackage{newtxtext}
\usepackage[libertine]{newtxmath}
\begin{document}
\begin{preview}
\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2
\end{preview}
\end{document}
! Missing $ inserted.
<inserted text>
$
l.12 \tfrac{1}{2}
mv^2
这样出错了。而改成一下这样就可以。
\[\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2\]
进行各种试探。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from latex2svg import latex2svg
file = open('The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 13_ Work and Potential Energy (A).html')
content = file.read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(content, features="lxml")
mathjaxs = soup.findAll('script', {'type': 'math/tex'})
for mathjax in mathjaxs:
print(mathjax.string)
wrap = '$' + mathjax.string + '$'
# if 'frac' in mathjax.string:
# wrap = '$' + mathjax.string + '$'
if 'FLP' in mathjax.string:
continue
elif 'Fig' in mathjax.string:
continue
elif 'eps' in mathjax.string:
continue
out = latex2svg(wrap)
# print(out)
node = BeautifulSoup(out['svg'], features="lxml")
svg = node.find('svg')
mathjax.insert_after(svg)
# print(out['svg'])
# break
# mathjax.replaceWith(out['svg'])
# print(dir(mathjax))
# break
# out = latex2svg(wrap)
# print(out['svg'])
# print(len(soup.contents))
output_file = open('out.html', 'w')
output_file.write(soup.prettify())
output_file.close()
# print(soup.contents)
# out = latex2svg(r'\( e^{i \pi} + 1 = 0 \)')
# print(out['depth'])
# print(out['svg'])
# svg = open('1.svg', 'w')
# svg.write(out['svg'])
# svg.close()
这些我都在试探什么呢。
if 'FLP' in mathjax.string:
continue
elif 'Fig' in mathjax.string:
continue
elif 'eps' in mathjax.string:
continue
这里当解析到有FLP、Fig、eps在latex源码的时候,转换的过程出错了。
例如,在HTML中,有这样的脚本:
<script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-11">\FLPF\cdot\FLPv</script>
解析拿到:
\FLPF\cdot\FLPv
当在代码里转换的时候出错了。也即,latex2svg.py出错了。这里就是用latex程序来转换。
code.tex:
\documentclass[12pt,preview]{standalone}
\usepackage[utf8x]{inputenc}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage{amsfonts}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\usepackage{newtxtext}
\usepackage[libertine]{newtxmath}
\begin{document}
\begin{preview}
\begin{equation}
\FLPF\cdot\FLPv
\end{equation}
\end{preview}
\end{document}
$latex code.tex
! Undefined control sequence.
l.13 \FLPF
\cdot\FLPv
?
这到底是什么问题。我后来才注意到在html中的这段代码。
<script type="text/x-mathjax-config;executed=true">
MathJax.Hub.Config({
TeX: {
Macros: {
FLPvec: ["\\boldsymbol{#1}", 1], Figvec: ["\\mathbf{#1}", 1], FLPC: ["\\FLPvec{C}", 0], FLPF: ["\\FLPvec{F}", 0], FLPa: ["\\FLPvec{a}", 0], FLPb: ["\\FLPvec{b}", 0], FLPr: ["\\FLPvec{r}", 0], FLPs: ["\\FLPvec{s}", 0], FLPv: ["\\FLPvec{v}", 0], ddt: ["\\frac{d#1}{d#2}", 2], epsO: ["\\epsilon_0", 0], FigC: ["\\Figvec{C}", 0]
}
}
});
</script>
这表示网页在渲染的时候,给MathJax设置上了宏。所以我们的latex转换源码里也应该加上。来加上它们。
\documentclass[12pt,preview]{standalone}
\usepackage[utf8x]{inputenc}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage{amsfonts}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\usepackage{newtxtext}
\usepackage[libertine]{newtxmath}
\newcommand{\FLPvec}[1]{\boldsymbol{#1}}
\newcommand{\Figvec}[1]{\mathbf{#1}}
\newcommand{\FLPC}{\FLPvec{C}}
\newcommand{\FLPF}{\FLPvec{F}}
\newcommand{\FLPa}{\FLPvec{a}}
\newcommand{\FLPb}{\FLPvec{a}}
\newcommand{\FLPr}{\FLPvec{r}}
\newcommand{\FLPs}{\FLPvec{s}}
\newcommand{\FLPv}{\FLPvec{v}}
\newcommand{\ddt}[2]{\frac{d#1}{d#2}}
\newcommand{\epsO}{\epsilon_0}
\newcommand{\FigC}{\Figvec{C}}
\begin{document}
\begin{preview}
\begin{equation}
\FLPF\cdot\FLPv
\end{equation}
\end{preview}
\end{document}
这样就对了。
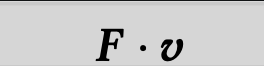
分析代码
来看看最后的代码。
import subprocess
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from latex2svg import latex2svg
def clean_mathjax(soup, name, cls):
previews = soup.findAll(name, {'class': cls})
for preview in previews:
preview.decompose()
def clean_script(soup):
scripts = soup.findAll('script')
for s in scripts:
s.decompose()
def wrap_latex(mathjax, equation = False):
wrap = ''
if equation:
wrap = mathjax.string
else:
wrap = '$' + mathjax.string + '$'
wrap = wrap.replace('label', 'tag')
return wrap
def wrap_svg(svg, equation):
if equation:
p = BeautifulSoup(f'<div style="text-align:center;"></div>', features="lxml")
p.div.append(svg)
return p.div
else:
return svg
def to_svg(mathjaxs, equation=False):
if equation:
svg_prefix = 'eq_'
else:
svg_prefix = 'in_'
i = 0
for mathjax in mathjaxs:
print(mathjax.string)
wrap = wrap_latex(mathjax, equation=equation)
out = {}
try:
out = latex2svg(wrap)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as err:
raise err
f = open(f'svgs/{svg_prefix}{i}.svg', 'w')
f.write(out['svg'])
f.close()
node = BeautifulSoup('<img>', features="lxml")
img = node.find('img')
img.attrs['src'] = f'./svgs/{svg_prefix}{i}.svg'
img.attrs['style'] = 'vertical-align: middle; margin: 0.5em 0;'
p = wrap_svg(img, equation)
mathjax.insert_after(p)
i +=1
def main():
file = open('The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 13_ Work and Potential Energy (A).html')
content = file.read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(content, features="lxml")
clean_mathjax(soup, 'span', 'MathJax')
clean_mathjax(soup, 'div', 'MathJax_Display')
clean_mathjax(soup, 'span', 'MathJax_Preview')
mathjaxs = soup.findAll('script', {'type': 'math/tex'})
to_svg(mathjaxs, equation=False)
mathjaxs = soup.findAll('script', {'type': 'math/tex; mode=display'})
to_svg(mathjaxs, equation=True)
clean_script(soup)
output_file = open('out.html', 'w')
output_file.write(soup.prettify())
output_file.close()
main()
当我们想转换整个电子书时,可以先用一个页面来试试。
file = open('The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 13_ Work and Potential Energy (A).html')
content = file.read()
这里便是下载了一个页面。
MathJax生成了很多的div和span。意思是比如 T+U=const。MathJax这样来生成。
<span class="MathJax">T</span>
<span class="MathJax">+</span>
<span class="MathJax">U</span>
<span class="MathJax">=</span>
<span class="MathJax">const</span>
这些很讨厌,也会影响我们的文本。因为已经有svg了,不需要这些了。
def clean_mathjax(soup, name, cls):
previews = soup.findAll(name, {'class': cls})
for preview in previews:
preview.decompose()
clean_mathjax(soup, 'span', 'MathJax')
clean_mathjax(soup, 'div', 'MathJax_Display')
clean_mathjax(soup, 'span', 'MathJax_Preview')
把它们都去掉。
mathjaxs = soup.findAll('script', {'type': 'math/tex'})
to_svg(mathjaxs, equation=False)
mathjaxs = soup.findAll('script', {'type': 'math/tex; mode=display'})
to_svg(mathjaxs, equation=True)
注意到这里分成两种的script。
m(dv/dt)=F
这是内嵌形式的。
\begin{equation}
\underset{\text{K.E.}}{\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2}+
\underset{\text{P.E.}}{\vphantom{\tfrac{1}{2}}mgh}=\text{const},\notag
这是成段形式的。
当时内嵌形式时,转换要在表达式左右加上$或[]。否则就有可能出错。
\begin{document}
\begin{preview}
\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2
\end{preview}
\end{document}
! Missing $ inserted.
<inserted text>
$
l.26 \tfrac{1}{2}
mv^2
得改成这样:
\begin{document}
\begin{preview}
$\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2$
\end{preview}
\end{document}
接下来看看如何转换latex成svg。
if equation:
svg_prefix = 'eq_'
else:
svg_prefix = 'in_'
% tree svgs
svgs
├── eq_0.svg
├── eq_1.svg
├── in_0.svg
这样来保存svg。
def wrap_latex(mathjax, equation = False):
wrap = ''
if equation:
wrap = mathjax.string
else:
wrap = '$' + mathjax.string + '$'
wrap = wrap.replace('label', 'tag')
return wrap
这里来对latex源码进行一些调整。注意到label变成了tag。
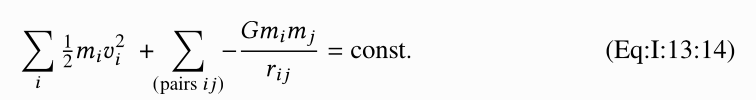
注意右边的(Eq:I:13:14)。如果是label的话,则没解析成功。这会显示的是(1)。这里将就用tag表示一下,暂时没有深究。
接着就进行调用latex2svg.py。
out = {}
try:
out = latex2svg(wrap)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as err:
raise err
看看latex2svg.py。
# Run LaTeX and create DVI file
try:
ret = subprocess.run(shlex.split(params['latex_cmd']+' code.tex'),
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
cwd=working_directory)
ret.check_returncode()
except FileNotFoundError:
raise RuntimeError('latex not found')
这里是在调用latex命令。
% latex --help
Usage: pdftex [OPTION]... [TEXNAME[.tex]] [COMMANDS]
or: pdftex [OPTION]... \FIRST-LINE
or: pdftex [OPTION]... &FMT ARGS
Run pdfTeX on TEXNAME, usually creating TEXNAME.pdf.
try:
ret = subprocess.run(shlex.split(params['dvisvgm_cmd']+' code.dvi'),
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
cwd=working_directory, env=env)
ret.check_returncode()
except FileNotFoundError:
raise RuntimeError('dvisvgm not found')
这里是在调用dvisvgm命令。
% dvisvgm
dvisvgm 2.9.1
This program converts DVI files, as created by TeX/LaTeX, as well as
EPS and PDF files to the XML-based scalable vector graphics format SVG.
Usage: dvisvgm [options] dvifile
dvisvgm --eps [options] epsfile
dvisvgm --pdf [options] pdffile
上面说的latex自定义宏写在哪儿呢。这里要改一下latex2svg.py。改改default_preamble。
default_preamble = r"""
\usepackage[utf8x]{inputenc}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage{amsfonts}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\usepackage{newtxtext}
\usepackage[libertine]{newtxmath}
\newcommand{\FLPvec}[1]{\boldsymbol{#1}}
\newcommand{\Figvec}[1]{\mathbf{#1}}
\newcommand{\FLPC}{\FLPvec{C}}
\newcommand{\FLPF}{\FLPvec{F}}
\newcommand{\FLPa}{\FLPvec{a}}
\newcommand{\FLPb}{\FLPvec{a}}
\newcommand{\FLPr}{\FLPvec{r}}
\newcommand{\FLPs}{\FLPvec{s}}
\newcommand{\FLPv}{\FLPvec{v}}
\newcommand{\ddt}[2]{\frac{d#1}{d#2}}
\newcommand{\epsO}{\epsilon_0}
\newcommand{\FigC}{\Figvec{C}}
"""
转换成功后,写入到文件。
f = open(f'svgs/{svg_prefix}{i}.svg', 'w')
f.write(out['svg'])
f.close()
继续。
node = BeautifulSoup('<img>', features="lxml")
img = node.find('img')
img.attrs['src'] = f'./svgs/{svg_prefix}{i}.svg'
img.attrs['style'] = 'vertical-align: middle; margin: 0.5em 0;'
这里构造一个img标签。
def wrap_svg(svg, equation):
if equation:
p = BeautifulSoup(f'<div style="text-align:center;"></div>', features="lxml")
p.div.append(svg)
return p.div
else:
return svg
p = wrap_svg(img, equation)
如果是独段的latex,那么用div包起来,并且居中。
mathjax.insert_after(p)
这里把div标签或img标签加在原来的script后面。
def clean_script(soup):
scripts = soup.findAll('script')
for s in scripts:
s.decompose()
clean_script(soup)
把所有的latex替换完svg后,就不需要script了。把它们删掉,这样整洁一点。
最后,再写入把修改后的整个html写入到一个文件里。
output_file = open('out.html', 'w')
output_file.write(soup.prettify())
output_file.close()
接着用pandoc工具,转换成epub。
pandoc -s -r html out.html -o feynman.epub
这会打开,就是漂亮的电子书了。
为什么不直接嵌入svg标签,而是用img来引入呢。即是说这样写:
<p></p>
<svg></svg>
<p></p>
有个很奇怪的bug。当有很多的svg的时候,会出现这样的情况。
后来发现用img引入就行。至于为什么这样,没搞明白。当我把这单个的svg拿出来的时候,用浏览器看就没有问题。看来是在浏览器渲染非常多个svg时,就会出错。
最后
至于epub如何转成mobi,可以用Kindle的官方工具Kindle Previewer 3。注意这里只是一章。
该项目代码在feynman-lectures-mobi@lzwjava。
如何把所有的页面都抓取整理成电子书呢。后续再讲。但这费曼物理讲义一章也够看的了。好了,让我们拿起Kindle开始看吧。