Python 编程之网上刷题
Home
这里我们用网上评测系统来做做题。英文好的话,可以用Codeforces和LeetCode。中文可以上计蒜客和力扣。这里用LeetCode。我这里做了10道题。同时最后1题采用了多种方法,把程序效率从击败10%的提交优化到了击败99%。
1480. Running Sum of 1d Array
Given an array
nums. We define a running sum of an array asrunningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i]).Return the running sum of
nums.
class Solution:
def runningSum(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
running = []
s = 0
for num in nums:
s += num
running.append(s)
return running
#print(Solution().runningSum([1,2,3,4]))
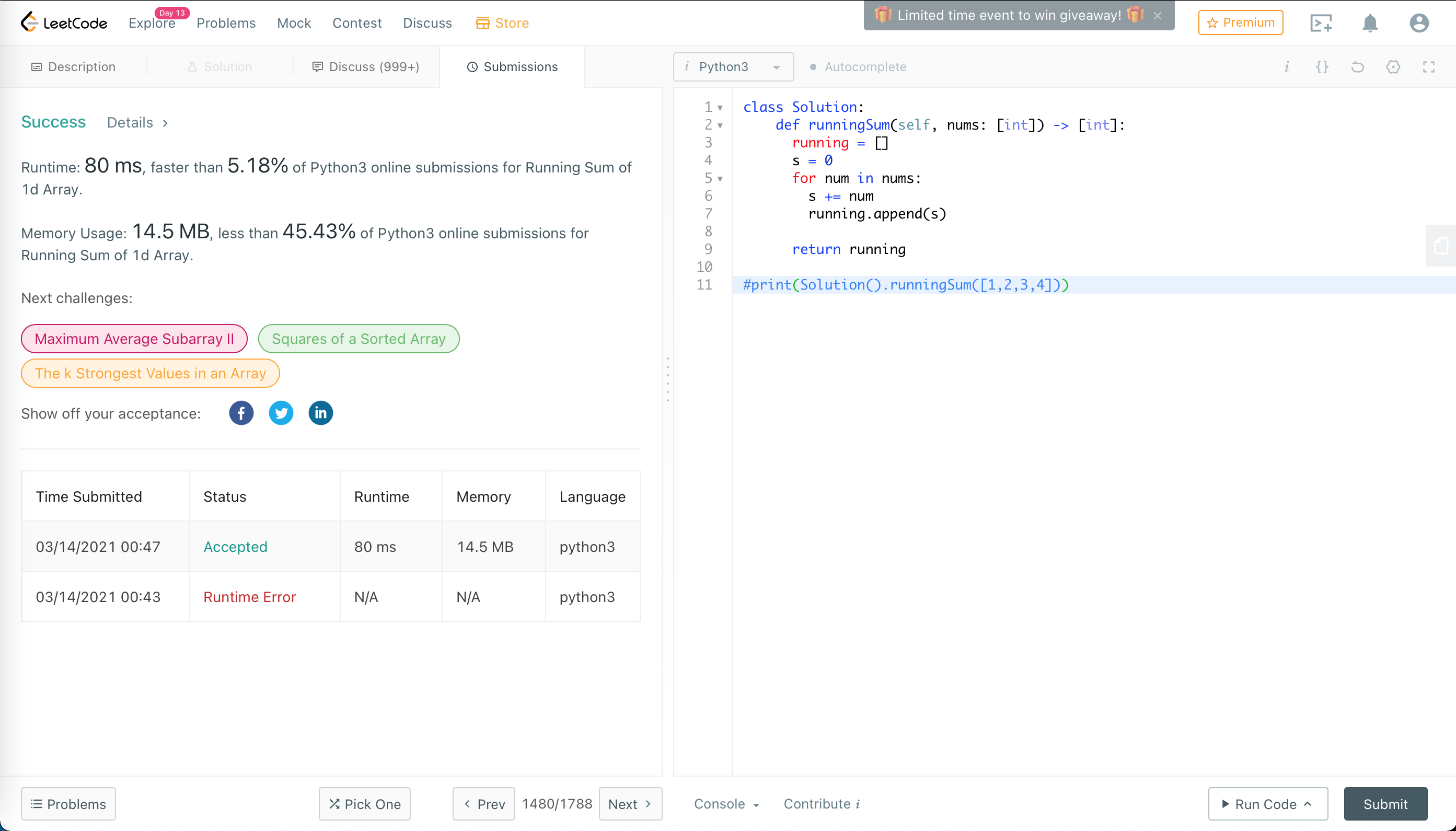
第一题通过。
1108. Defanging an IP Address
Given a valid (IPv4) IP
address, return a defanged version of that IP address.A defanged IP address replaces every period
"."with"[.]".
class Solution:
def defangIPaddr(self, address: str) -> str:
return address.replace('.', '[.]')
# print(Solution().defangIPaddr('1.1.1.1'))
1431. Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies
Given the array
candiesand the integerextraCandies, wherecandies[i]represents the number of candies that the *ith* kid has.For each kid check if there is a way to distribute
extraCandiesamong the kids such that he or she can have the greatest number of candies among them. Notice that multiple kids can have the greatest number of candies.
class Solution:
def kidsWithCandies(self, candies: [int], extraCandies: int) -> [bool]:
max = 0
for candy in candies:
if candy > max:
max = candy
greatests = []
for candy in candies:
if candy + extraCandies >= max:
greatests.append(True)
else:
greatests.append(False)
return greatests
# print(Solution().kidsWithCandies([2,3,5,1,3], 3))
1672. Richest Customer Wealth
You are given an
m x ninteger gridaccountswhereaccounts[i][j]is the amount of money theithcustomer has in thejthbank. Return the wealth that the richest customer has.A customer’s wealth is the amount of money they have in all their bank accounts. The richest customer is the customer that has the maximum wealth.
class Solution:
def maximumWealth(self, accounts: [[int]]) -> int:
max = 0
for account in accounts:
s = sum(account)
if max < s:
max = s
return max
#print(Solution().maximumWealth([[1,2,3],[3,2,1]]))
1470. Shuffle the Array
Given the array
numsconsisting of2nelements in the form[x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn].Return the array in the form
[x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].
class Solution:
def shuffle(self, nums: [int], n: int) -> [int]:
ns1 = nums[:n]
ns2 = nums[n:]
ns = []
for i in range(n):
ns.append(ns1[i])
ns.append(ns2[i])
return ns
# print(Solution().shuffle([2,5,1,3,4,7], 3))
1512. Number of Good Pairs
Given an array of integers
nums.A pair
(i,j)is called good ifnums[i]==nums[j]andi<j.Return the number of good pairs.
class Solution:
def numIdenticalPairs(self, nums: [int]) -> int:
j = 1
n = len(nums)
p = 0
while j < n:
for i in range(j):
if nums[i] == nums[j]:
p += 1
j+=1
return p
# print(Solution().numIdenticalPairs([1,2,3,1,1,3]))
771. Jewels and Stones
You’re given strings
jewelsrepresenting the types of stones that are jewels, andstonesrepresenting the stones you have. Each character instonesis a type of stone you have. You want to know how many of the stones you have are also jewels.Letters are case sensitive, so
"a"is considered a different type of stone from"A".
class Solution:
def numJewelsInStones(self, jewels: str, stones: str) -> int:
n = 0
for i in range(len(jewels)):
js = jewels[i:i+1]
n += stones.count(js)
return n
# print(Solution().numJewelsInStones("aA", "aAAbbbb"))
1603. Design Parking System
Design a parking system for a parking lot. The parking lot has three kinds of parking spaces: big, medium, and small, with a fixed number of slots for each size.
Implement the
ParkingSystemclass:
ParkingSystem(int big, int medium, int small)Initializes object of theParkingSystemclass. The number of slots for each parking space are given as part of the constructor.bool addCar(int carType)Checks whether there is a parking space ofcarTypefor the car that wants to get into the parking lot.carTypecan be of three kinds: big, medium, or small, which are represented by1,2, and3respectively. A car can only park in a parking space of itscarType. If there is no space available, returnfalse, else park the car in that size space and returntrue.
class ParkingSystem:
slots = [0, 0, 0]
def __init__(self, big: int, medium: int, small: int):
self.slots[0] = big
self.slots[1] = medium
self.slots[2] = small
def addCar(self, carType: int) -> bool:
if self.slots[carType - 1] > 0:
self.slots[carType - 1] -=1
return True
else:
return False
# parkingSystem = ParkingSystem(1, 1, 0)
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(1))
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(2))
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(3))
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(1))
1773. Count Items Matching a Rule
You are given an array
items, where eachitems[i] = [typei, colori, namei]describes the type, color, and name of theithitem. You are also given a rule represented by two strings,ruleKeyandruleValue.The
ithitem is said to match the rule if one of the following is true:
ruleKey == "type"andruleValue == typei.ruleKey == "color"andruleValue == colori.ruleKey == "name"andruleValue == namei.Return the number of items that match the given rule.
class Solution:
def countMatches(self, items: [[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:
i = 0
if ruleKey == "type":
i = 0
elif ruleKey == "color":
i = 1
else:
i = 2
n = 0
for item in items:
if item[i] == ruleValue:
n +=1
return n
# print(Solution().countMatches([["phone","blue","pixel"],["computer","silver","lenovo"],["phone","gold","iphone"]], "color", "silver"))
1365. How Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number
Given the array
nums, for eachnums[i]find out how many numbers in the array are smaller than it. That is, for eachnums[i]you have to count the number of validj'ssuch thatj != iandnums[j] < nums[i].Return the answer in an array.
Input: nums = [8,1,2,2,3] Output: [4,0,1,1,3] Explanation: For nums[0]=8 there exist four smaller numbers than it (1, 2, 2 and 3). For nums[1]=1 does not exist any smaller number than it. For nums[2]=2 there exist one smaller number than it (1). For nums[3]=2 there exist one smaller number than it (1). For nums[4]=3 there exist three smaller numbers than it (1, 2 and 2).
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ns = []
l = len(nums)
for i in range(l):
n = 0
for j in range(l):
if i != j:
if nums[j] < nums[i]:
n += 1
ns.append(n)
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
用时528ms,击败了11.81%的程序。优化一下。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
sort_nums = nums.copy()
ins = list(range(l))
for i in range(l):
for j in range(i+1, l):
if sort_nums[i] > sort_nums[j]:
a = sort_nums[i]
sort_nums[i] = sort_nums[j]
sort_nums[j] = a
a = ins[i]
ins[i] = ins[j]
ins[j] = a
smalls = [0]
for i in range(1, l):
if sort_nums[i-1] == sort_nums[i]:
smalls.append(smalls[i-1])
else:
smalls.append(i)
# print(sort_nums)
# print(smalls)
r_is = list(range(l))
for i in ins:
r_is[ins[i]] = i
ns = []
for i in range(l):
ns.append(smalls[r_is[i]])
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
这会测试用时284ms,比刚刚用时528ms少。
用写系统的函数简写一下。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
sort_nums = nums.copy()
sort_nums.sort()
ns = []
for num in nums:
ns.append(sort_nums.index(num))
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
这会只需用时64ms,击败了71%的提交。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
ns = [0] * l
for i in range(l):
for j in range(i+1, l):
if nums[i] > nums[j]:
ns[i] +=1
elif nums[i] < nums[j]:
ns[j] +=1
else:
pass
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
又想出来一种解法。用时400ms。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ss = sorted((e,i) for i,e in enumerate(nums))
l = len(nums)
smalls = [0]
for i in range(1, l):
(e0, j0) = ss[i-1]
(e1, j1) = ss[i]
if e0 == e1:
smalls.append(smalls[i-1])
else:
smalls.append(i)
ns = [0]*l
for i in range(l):
(e,j) = ss[i]
ns[j] = smalls[i]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
Runtime: 52 ms, faster than 91.45% of Python3 online submissions forHow Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
Memory Usage: 14.6 MB, less than 15.18% of Python3 online submissions for How Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
终于成功了!这个方法又更快了,打败了91.45%的提交。
继续精简一下。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ss = sorted((e,i) for i,e in enumerate(nums))
l = len(nums)
smalls = [0]
ns = [0]*l
for i in range(1, l):
(e0, j0) = ss[i-1]
(e1, j1) = ss[i]
if e0 == e1:
smalls.append(smalls[i-1])
else:
smalls.append(i)
ns[j1] = smalls[i]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
继续。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ss = sorted((e,i) for i,e in enumerate(nums))
l = len(nums)
last = 0
ns = [0]*l
for i in range(1, l):
(e0, j0) = ss[i-1]
(e1, j1) = ss[i]
if e0 == e1:
pass
else:
last = i
ns[j1] = last
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
这时我们跑到了40ms,击败了99.81%程序。
Runtime: 40 ms, faster than 99.81% of Python3 online submissions forHow Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
Memory Usage: 14.4 MB, less than 15.18% of Python3 online submissions for How Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
再来一种解法。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
n = [0] * 101
max_num = 0
for num in nums:
n[num] += 1
if num > max_num:
max_num = num
sm = [0] * (max_num + 1)
sum = 0
for i in range(max_num+1):
sm[i] = sum
sum += n[i]
ns = [0] * l
for i in range(l):
ns[i] = sm[nums[i]]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
来个稍微复杂的。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
n = [0] * 101
max_num = 0
for num in nums:
n[num] += 1
if num > max_num:
max_num = num
short_n = []
short_num = [] * l
zn = [0] * 101
j = 0
for i in range(max_num+1):
if n[i] > 0:
zn[i] = j
short_n.append(n[i])
short_num.append(num)
j+=1
sm = [0] * j
sum = 0
for i in range(j):
sm[i] = sum
sum += short_n[i]
ns = [0] * l
for i in range(l):
ns[i] = sm[zn[nums[i]]]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
max_num =max(nums)
n = [0] * (max_num + 1)
for num in nums:
n[num] += 1
sorted_ls = []
for i in range(max_num + 1):
if n[i] > 0:
sorted_ls.append(i)
sm = [0] * (max_num + 1)
sum = 0
for i in range(len(sorted_ls)):
v = sorted_ls[i]
sm[v] = sum
sum += n[v]
ns = []
for i in range(len(nums)):
ns.append(sm[nums[i]])
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([72,48,32,16,10,59,83,38,1,4,68,7,67,16,5,35,99,15,55,11,24,3,63,81,16,95,35,87,24,84,57,49,42,80,34,33,82,81,31,31,7,75,100,75,22,44,54,77,89,71,81,66,7]))
练习
- 学生像上面这样类似刷上一些题目。