Python 編程之網上刷題 | 原創,AI翻譯
這裡我們用網上評測系統來做做題。英文好的話,可以用Codeforces和LeetCode。中文可以上計蒜客和力扣。這裡用LeetCode。我這裡做了10道題。同時最後1題採用了多種方法,把程序效率從擊敗10%的提交優化到了擊敗99%。
1480. 一維陣列的運行總和
給定一個陣列
nums。我們定義一個陣列的運行總和為runningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i])。返回
nums的運行總和。
class Solution:
def runningSum(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
running = []
s = 0
for num in nums:
s += num
running.append(s)
return running
#print(Solution().runningSum([1,2,3,4]))
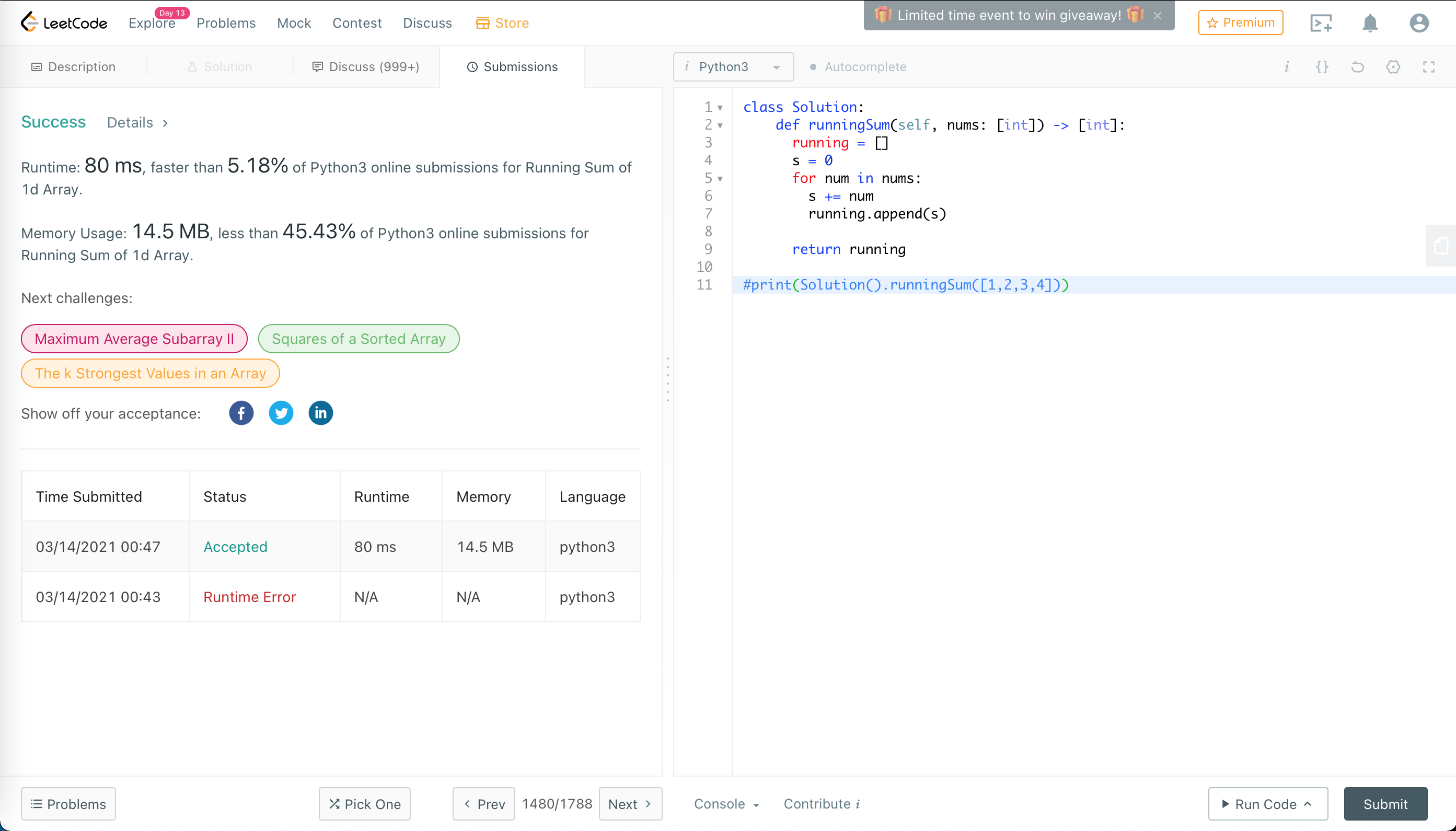
第一題通過。
1108. 替換IP地址中的句點
給定一個有效的(IPv4)IP地址
address,返回該IP地址的替換版本。一個替換的IP地址將每個句點
"."替換為"[.]"。
class Solution:
def defangIPaddr(self, address: str) -> str:
return address.replace('.', '[.]')
# print(Solution().defangIPaddr('1.1.1.1'))
1431. 擁有最多糖果的孩子
給定陣列
candies和整數extraCandies,其中candies[i]表示第i個孩子擁有的糖果數量。對於每個孩子,檢查是否存在一種分配
extraCandies的方法,使得他或她可以擁有最多的糖果。注意,多個孩子可以擁有最多的糖果。
class Solution:
def kidsWithCandies(self, candies: [int], extraCandies: int) -> [bool]:
max = 0
for candy in candies:
if candy > max:
max = candy
greatests = []
for candy in candies:
if candy + extraCandies >= max:
greatests.append(True)
else:
greatests.append(False)
return greatests
# print(Solution().kidsWithCandies([2,3,5,1,3], 3))
1672. 最富有客戶的資產
給定一個
m x n的整數網格accounts,其中accounts[i][j]是第i個客戶在第j個銀行中的金額。返回最富有客戶的資產。客戶的資產是他們在所有銀行帳戶中的金額總和。最富有的客戶是擁有最大資產的客戶。
class Solution:
def maximumWealth(self, accounts: [[int]]) -> int:
max = 0
for account in accounts:
s = sum(account)
if max < s:
max = s
return max
#print(Solution().maximumWealth([[1,2,3],[3,2,1]]))
1470. 重新排列陣列
給定一個由
2n個元素組成的陣列nums,形式為[x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn]。返回陣列的形式為
[x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn]。
class Solution:
def shuffle(self, nums: [int], n: int) -> [int]:
ns1 = nums[:n]
ns2 = nums[n:]
ns = []
for i in range(n):
ns.append(ns1[i])
ns.append(ns2[i])
return ns
# print(Solution().shuffle([2,5,1,3,4,7], 3))
1512. 好數對的數量
給定一個整數陣列
nums。如果
nums[i]==nums[j]且i<j,則稱(i,j)為好數對。返回好數對的數量。
class Solution:
def numIdenticalPairs(self, nums: [int]) -> int:
j = 1
n = len(nums)
p = 0
while j < n:
for i in range(j):
if nums[i] == nums[j]:
p += 1
j+=1
return p
# print(Solution().numIdenticalPairs([1,2,3,1,1,3]))
771. 寶石與石頭
給定字符串
jewels表示寶石的類型,和stones表示你擁有的石頭。stones中的每個字符代表你擁有的一種石頭。你想知道你擁有的石頭中有多少是寶石。字母區分大小寫,所以
"a"被認為是不同於"A"的石頭類型。
class Solution:
def numJewelsInStones(self, jewels: str, stones: str) -> int:
n = 0
for i in range(len(jewels)):
js = jewels[i:i+1]
n += stones.count(js)
return n
# print(Solution().numJewelsInStones("aA", "aAAbbbb"))
1603. 設計停車系統
為停車場設計一個停車系統。停車場有三種停車位:大、中、小,每種大小有固定數量的停車位。
實現
ParkingSystem類:
ParkingSystem(int big, int medium, int small)初始化ParkingSystem類的對象。每種停車位的數量作為構造函數的一部分給出。bool addCar(int carType)檢查是否有carType類型的停車位可供汽車進入停車場。carType可以是三種類型:大、中、小,分別用1、2和3表示。汽車只能停在與其carType匹配的停車位。如果沒有可用的停車位,返回false,否則將汽車停在該大小的停車位並返回true。
class ParkingSystem:
slots = [0, 0, 0]
def __init__(self, big: int, medium: int, small: int):
self.slots[0] = big
self.slots[1] = medium
self.slots[2] = small
def addCar(self, carType: int) -> bool:
if self.slots[carType - 1] > 0:
self.slots[carType - 1] -=1
return True
else:
return False
# parkingSystem = ParkingSystem(1, 1, 0)
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(1))
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(2))
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(3))
# print(parkingSystem.addCar(1))
1773. 統計匹配規則的項目數量
給定一個陣列
items,其中每個items[i] = [typei, colori, namei]描述了第i個項目的類型、顏色和名稱。你還給定一個由兩個字符串ruleKey和ruleValue表示的規則。如果滿足以下條件之一,則第
i個項目被認為匹配該規則:
ruleKey == "type"且ruleValue == typei。ruleKey == "color"且ruleValue == colori。ruleKey == "name"且ruleValue == namei。返回匹配給定規則的項目數量。
class Solution:
def countMatches(self, items: [[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:
i = 0
if ruleKey == "type":
i = 0
elif ruleKey == "color":
i = 1
else:
i = 2
n = 0
for item in items:
if item[i] == ruleValue:
n +=1
return n
# print(Solution().countMatches([["phone","blue","pixel"],["computer","silver","lenovo"],["phone","gold","iphone"]], "color", "silver"))
1365. 有多少小於當前數字的數字
給定陣列
nums,對於每個nums[i],找出陣列中有多少數字小於它。也就是說,對於每個nums[i],你需要計算滿足j != i且nums[j] < nums[i]的有效j的數量。以陣列形式返回答案。
輸入: nums = [8,1,2,2,3] 輸出: [4,0,1,1,3] 解釋: 對於nums[0]=8,有四個數字小於它(1, 2, 2和3)。 對於nums[1]=1,沒有數字小於它。 對於nums[2]=2,有一個數字小於它(1)。 對於nums[3]=2,有一個數字小於它(1)。 對於nums[4]=3,有三個數字小於它(1, 2和2)。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ns = []
l = len(nums)
for i in range(l):
n = 0
for j in range(l):
if i != j:
if nums[j] < nums[i]:
n += 1
ns.append(n)
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
用時528ms,擊敗了11.81%的程序。優化一下。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
sort_nums = nums.copy()
ins = list(range(l))
for i in range(l):
for j in range(i+1, l):
if sort_nums[i] > sort_nums[j]:
a = sort_nums[i]
sort_nums[i] = sort_nums[j]
sort_nums[j] = a
a = ins[i]
ins[i] = ins[j]
ins[j] = a
smalls = [0]
for i in range(1, l):
if sort_nums[i-1] == sort_nums[i]:
smalls.append(smalls[i-1])
else:
smalls.append(i)
# print(sort_nums)
# print(smalls)
r_is = list(range(l))
for i in ins:
r_is[ins[i]] = i
ns = []
for i in range(l):
ns.append(smalls[r_is[i]])
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
這會測試用時284ms,比剛剛用時528ms少。
用寫系統的函數簡寫一下。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
sort_nums = nums.copy()
sort_nums.sort()
ns = []
for num in nums:
ns.append(sort_nums.index(num))
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
這會只需用時64ms,擊敗了71%的提交。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
ns = [0] * l
for i in range(l):
for j in range(i+1, l):
if nums[i] > nums[j]:
ns[i] +=1
elif nums[i] < nums[j]:
ns[j] +=1
else:
pass
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
又想出來一種解法。用時400ms。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ss = sorted((e,i) for i,e in enumerate(nums))
l = len(nums)
smalls = [0]
for i in range(1, l):
(e0, j0) = ss[i-1]
(e1, j1) = ss[i]
if e0 == e1:
smalls.append(smalls[i-1])
else:
smalls.append(i)
ns = [0]*l
for i in range(l):
(e,j) = ss[i]
ns[j] = smalls[i]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
Runtime: 52 ms, faster than 91.45% of Python3 online submissions forHow Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
Memory Usage: 14.6 MB, less than 15.18% of Python3 online submissions for How Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
終於成功了!這個方法又更快了,打敗了91.45%的提交。
繼續精簡一下。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ss = sorted((e,i) for i,e in enumerate(nums))
l = len(nums)
smalls = [0]
ns = [0]*l
for i in range(1, l):
(e0, j0) = ss[i-1]
(e1, j1) = ss[i]
if e0 == e1:
smalls.append(smalls[i-1])
else:
smalls.append(i)
ns[j1] = smalls[i]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
繼續。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
ss = sorted((e,i) for i,e in enumerate(nums))
l = len(nums)
last = 0
ns = [0]*l
for i in range(1, l):
(e0, j0) = ss[i-1]
(e1, j1) = ss[i]
if e0 == e1:
pass
else:
last = i
ns[j1] = last
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
這時我們跑到了40ms,擊敗了99.81%程序。
Runtime: 40 ms, faster than 99.81% of Python3 online submissions forHow Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
Memory Usage: 14.4 MB, less than 15.18% of Python3 online submissions for How Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number.
再來一種解法。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
n = [0] * 101
max_num = 0
for num in nums:
n[num] += 1
if num > max_num:
max_num = num
sm = [0] * (max_num + 1)
sum = 0
for i in range(max_num+1):
sm[i] = sum
sum += n[i]
ns = [0] * l
for i in range(l):
ns[i] = sm[nums[i]]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
來個稍微複雜的。
class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
l = len(nums)
n = [0] * 101
max_num = 0
for num in nums:
n[num] += 1
if num > max_num:
max_num = num
short_n = []
short_num = [] * l
zn = [0] * 101
j = 0
for i in range(max_num+1):
if n[i] > 0:
zn[i] = j
short_n.append(n[i])
short_num.append(num)
j+=1
sm = [0] * j
sum = 0
for i in range(j):
sm[i] = sum
sum += short_n[i]
ns = [0] * l
for i in range(l):
ns[i] = sm[zn[nums[i]]]
return ns
# print(Solution().smallerNumbersThanCurrent([8,1,2,2,3]))
```python class Solution:
def smallerNumbersThanCurrent(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
max_num =max(nums)
n = [0] * (max_num + 1)
for num in nums:
n[num] += 1
sorted_ls = []
for i in range(max_num + 1):
if n[i] > 0:
sorted_ls.append(i)
sm = [0] * (max_num + 1)
sum = 0
for i in range(len(sorted_ls)):
v = sorted_ls[i]
sm[v] = sum
sum += n[v]
ns = []